European Supervisory Authorities
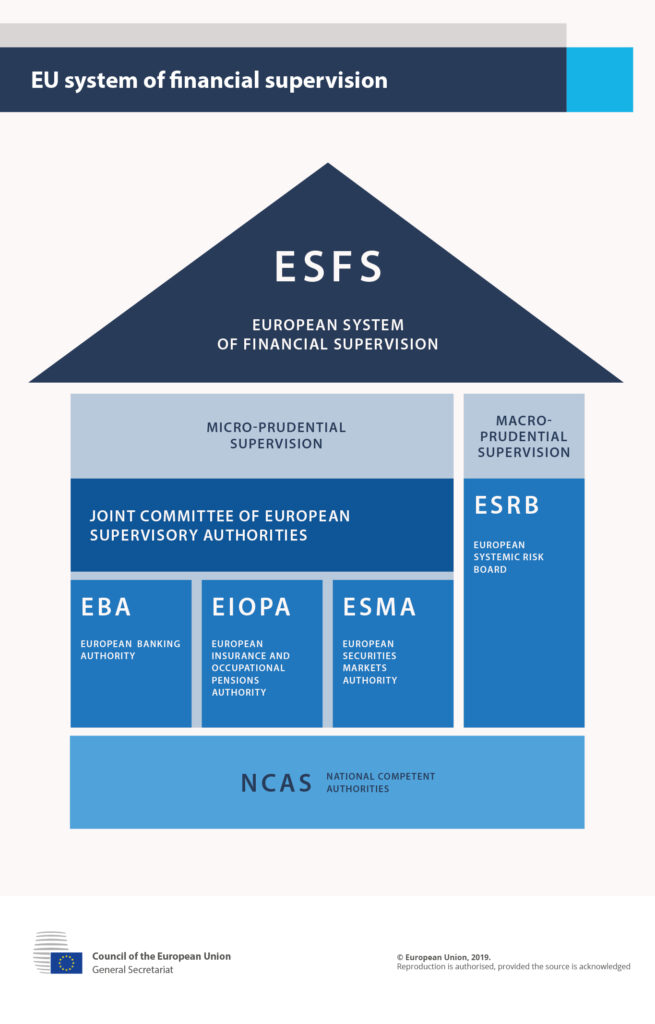
The European System of Financial Supervision is composed by three supervisory authorities (ESAs): the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), the European Banking Authority (EBA) and the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA).
ESMA
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) is an independent European Union (EU) Authority that contributes to safeguarding the stability of the EU’s financial system by enhancing the protection of investors and promoting stable and orderly financial markets.
ESMA achieves its objectives by assessing risks to investors, markets and financial stability; completing a single rulebook for EU financial markets; promoting supervisory convergence; and directly supervising credit rating agencies, trade repositories and securitisation repositories. ESMA, as well as fostering supervisory convergence amongst Member States’ national competent authorities (NCAs) with responsibility for securities and capital markets supervision, it aims to do so across financial sectors by working closely with the other European Supervisory Authorities competent in the field of banking (EBA), and insurance and occupational pensions (EIOPA).
Whilst ESMA is an independent Authority, it is accountable to the European Institutions including the European Parliament, where it appears before the Economic and Monetary Affairs Committee (ECON) at their request for formal hearings, the Council of the European Union and European Commission. The Authority reports to the institutions on its activities regularly at meetings and also through its Annual Report.
You can find further information about ESMA on its website: European Securities and Markets Authority – ESMA
EBA
The European Banking Authority (EBA) is an independent EU Authority which works to ensure effective and consistent prudential regulation and supervision across the European banking sector. Its overall objectives are to maintain financial stability in the EU and to safeguard the integrity, efficiency and orderly functioning of the banking sector.
The main task of the EBA is to contribute to the creation of the European Single Rulebook in banking whose objective is to provide a single set of harmonised prudential rules for financial institutions throughout the EU. The Authority also plays an important role in promoting convergence of supervisory practices and is mandated to assess risks and vulnerabilities in the EU banking sector.
The EBA was established on 1 January 2011 as part of the European System of Financial Supervision (ESFS) and took over all existing responsibilities and tasks of the Committee of European Banking Supervisors.
You can find further information about EBA on its website: European Banking Authority – EBA
EIOPA
The European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA) is a European Union financial regulatory institution.
EIOPA’s mission is to protect the public interest by contributing to the short, medium and long-term stability and effectiveness of the financial system for the Union economy, its citizens and businesses. This mission is pursued by promoting a sound regulatory framework and consistent supervisory practices in order to protect the rights of policyholders, pension scheme members and beneficiaries and contribute to the public confidence in the European Union’s insurance and occupational pensions sectors.
EIOPA is an independent advisory body to the European Commission, the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. It is one of the EU Agencies carrying out specific legal, technical or scientific tasks and giving evidence-based advice to help shape informed policies and laws at the EU and national level.
You can find further information about EIOPA on its website: European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority – EIOPA

